Genomic evidence of past and future climate-linked loss in a migratory Arctic fish
Genomic evidence of past and future climate-linked loss in a migratory Arctic fish
Abstract
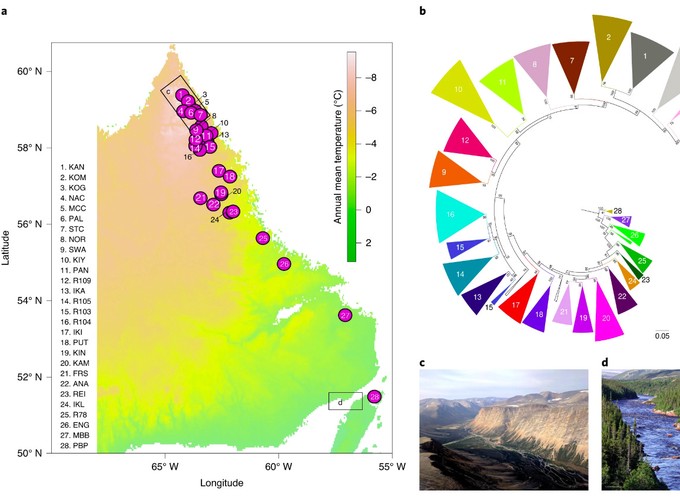
Despite widespread biodiversity losses, an understanding of how most taxa will respond to future climate change is lacking. Here we integrate genomics and environmental modelling to assess climate change responses in an ecologically and economically important Arctic species. Environmentally associated genomic diversity and machine learning are used to identify highly vulnerable populations of anadromous (migratory) Arctic charr, and we reconstruct estimates of effective population size spanning the twentieth century to identify past climate-associated declines. We uncover past region-wide declines in effective population size that correspond to decreases in temperature and community biomass in the Northwest Atlantic. We find vulnerable populations near the southern range limit, indicating northward shifts and a possible loss of commercially important life-history variation in response to climate change. The genomic approach used here to investigate climate change response identifies past and future declines that impact species persistence, ecosystem stability and food security in the Arctic.